One of the most overlooked medicinal herbs is Cannabis! I figured I’d type it out for EVERYONE to see some of the science behind this wonderful plant! You wouldn’t go into a pharmacy and just start eating pills, would you? So why would you go into a Dispensary and just pick out some weed? ALL herbs are powerful medicine, and should be taken seriously! I’ve had clients come to me with horrible anxiety inability to sleep and crazy rage and panic attacks. Come to find out they had picked up a weed strain WAY too strong for their system. We had some gut issues to address to, it wasn’t all the wrong weed.
What to Expect
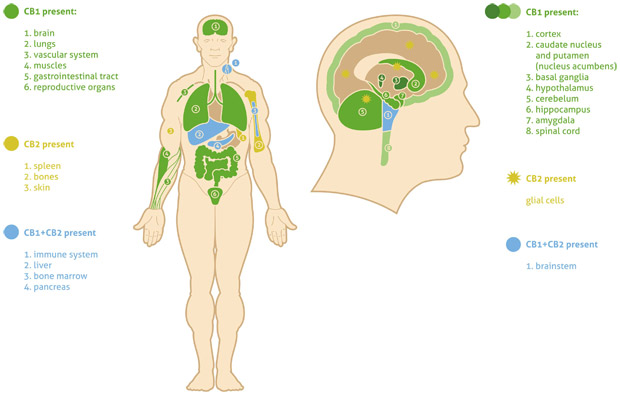
For in-office testing, I have energetic vials that would match the cannabinoid subclasses of at least 10 strains. I will be looking at CB1 and CB2 receptors, as well as a combination of CB1 & CB2, and the five major terpenes found in cannabis.
I will be looking for or testing to see which Cannabis strain balances the subclasses. I have samples of products that would best represent a fit for each class: Indica, Sativa, and significant strains. We may also consider other herbs that contain cannabinoids (such as Echinacea) or have an effect on cannabinoids (like green tea, turmeric, peppers, and EFA’s). However, first, we will be assessing your overall health to determine if cannabis is suitable for you. Once we establish that, you can visit your local dispensary to find the product that suits your needs. Please note that I do not sell cannabis in my office, but I can assist you in determining if it is necessary for you.
All About Cannabinoids
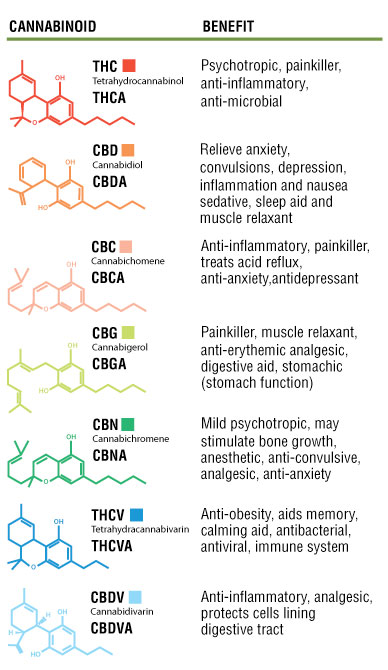
There are over 480 natural components found within the Cannabis sativa plant, of which 66 have been classified as “cannabinoids,” chemicals unique to the plant. The most well-known and researched of these is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), which is the substance primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis.
The effects of THC are believed to be moderated by the influence of the other components of the plant, particularly the cannabinoids.
The cannabinoids are separated into subclasses. These are as follows:
- Cannabigerols (CBG);
- Cannabichromenes (CBC);
- Cannabidiols (CBD);
- Tetrahydrocannabinols (THC);
- Cannabinol (CBN) and cannabinodiol (CBDL);
- Other cannabinoids (such as cannabicyclol (CBL), cannabielsoin (CBE), cannabitriol (CBT) and other miscellaneous types:).
What Do Cannabinoids Do?
Like opiates (substances derived from the opium poppy, such as heroin), cannabinoids affect the user by interacting with specific receptors located within different parts of the central nervous system. Two kinds of cannabinoid receptors have been found to date and are termed CB1 and CB2.
A substance that occurs naturally within the brain and binds to CB1 receptors was discovered in 1992 and termed “anandamide.” Additional naturally occurring substances that bind to CB1 have since been discovered, and these, together with the receptors, are termed the “endogenous cannabinoid system.”
The actual effects that cannabinoids have reflect the areas of the brain they interact with. Interactions tend to occur in our limbic system (the part of the brain that affects memory, cognition, and psychomotor performance) and the mesolimbic pathway (activity in this region is associated with feelings of reward) and are also widely distributed in areas of pain perception.
We are still learning about the endogenous cannabinoid system. Much of the research, however, has focused on the many potential medical uses of synthetic analogues, which are man-made cannabinoids.
What Is The Difference Between Cannabinoids?
The major differences between the cannabinoids are determined by the extent to which they are psychologically active. Three classes of cannabinoids, the CBG, CBC, and CBD are not known to have such an effect. THC, CBN, CBDL, and some other cannabinoids, on the other hand, are known to be psychologically active to varying degrees.
CBD is probably the most abundant cannabinoid, contributing up to 40% of cannabis resin. Interestingly, CBD may have anti-anxiety effects and lessen the psychoactive effects of THC. This means that a plant with a greater percentage of CBD may reduce the intensity of the effects of the THC, which in effect lowers the potency of the plant. Use of a cannabis plant with less CBD has been shown to have an increased psychological impact and result in unwanted effects such as anxiety.
When THC is exposed to air it oxidizes and forms CBN. CBN is only very weakly psychoactive and not unlike CBD
interacts with THC to reduce its effects. This is why cannabis that has been left out unused will have increasing amounts of CBN and decreasing amounts of THC and thus lose potency.
Some of this information was prepared by the National Cannabis Prevention and Information Centre in Australia and used with permission. Some information may not be accurate for U.S. readers.
If you’re interested in learning more about the medicinal benefits of cannabis and how it may be able to help you, I invite you to schedule a session with me. Together, we can explore your unique needs and determine if cannabis is the right option for you. Don’t hesitate to take control of your health and discover the potential of this incredible plant.